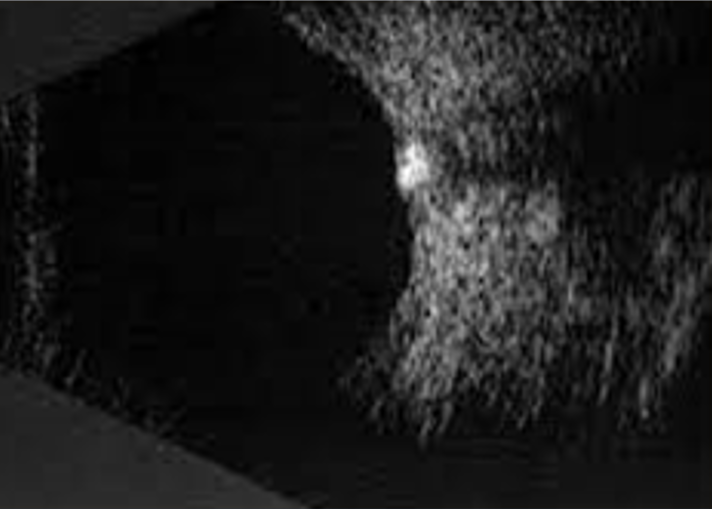
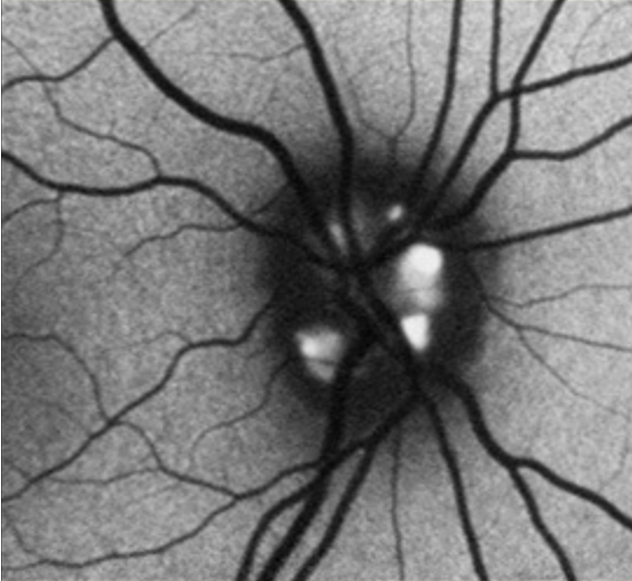
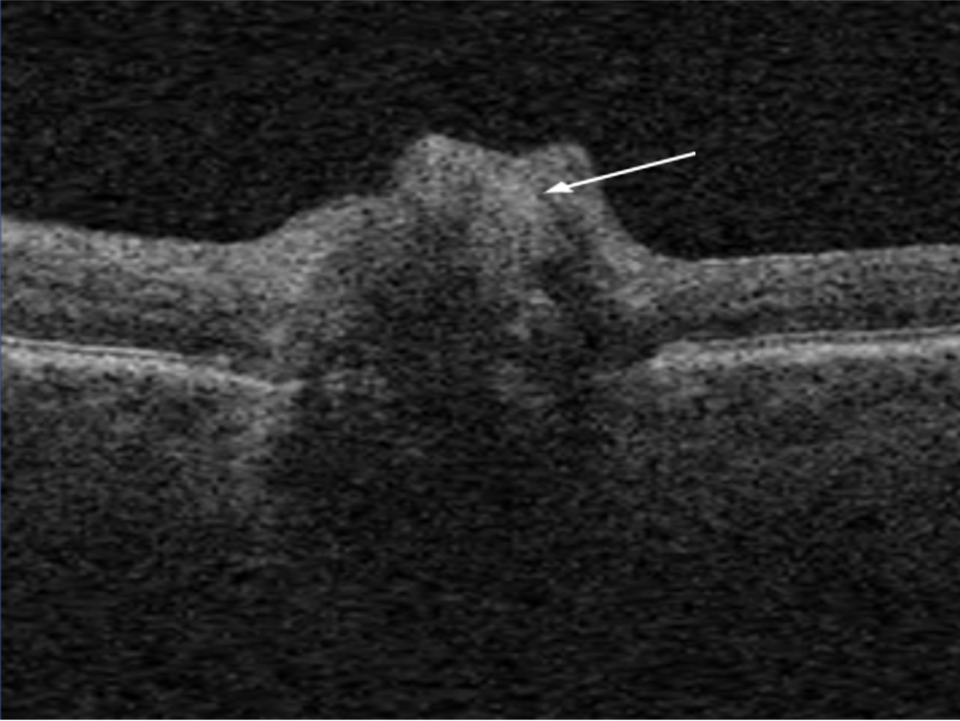
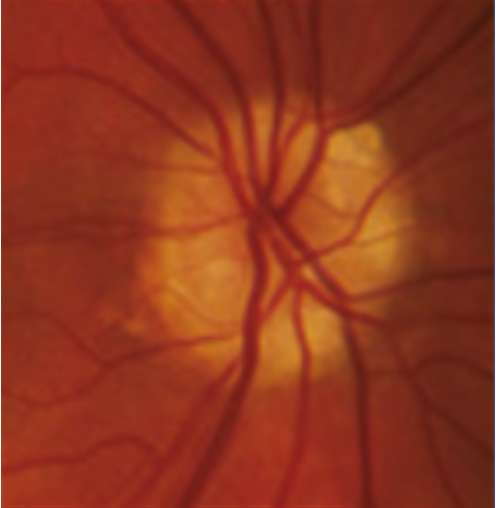
Optic disc drusen are accidental findings during an eye examination and represent acellular concretions predominantly made up of calcium, but can also contain amino and nucleic acids, mucopolysaccharides, and iron.(1)1 The primary pathogenesis of optic disc drusen remains unknown, with some hypothesising to be related to possibly inherited dysplasia of the optic disc with blood supply comprises, causing slowed axoplasmic flow and leading to the formation of calcific excrescences. (2,3) The optic disc drusen can be unilateral or bilateral, and according to literature, the vast majority are bilateral cases, and more often in females.(1) The reported prevalence of optic disc drusen is 1 to 500.(4)
Optic disc drusen can appear similar to papilloedema. This presentation is called pseudopapilloedema, and must be distinguished from actual optic disc oedema when examining these patients.